Learning Management System (LMS) Statistics 2023

Written by Casey Botticello
Disclosure: Some of the links below are affiliate links, meaning that at no additional cost to you, I will receive a commission if you click through and make a purchase. Read our full affiliate disclosure here.
Here is an interesting fact: Did you know that a single online course can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 85% when compared to in-person training? Yep, digital learning appears to be better for the environment than attending school in the traditional manner.
That’s one good reason why online learning has become increasingly important in recent years. Another factor that has triggered a boom in the e-Learning and LMS software market is the COVID-19 pandemic.
Curious about all that is happening in this educational segment and how it is changing the world and impacting online communities? This article provides a deep dive into some of the most interesting statistics surrounding digital learning.
What impact is LMS and e-Learning software having on schools and the workplace? What are some of the ways people are making use of online learning, and what platforms are facilitating this shift? What is the outlook for the future of e-Learning?
LMS Landscape and Statistics 2023

1. LMS and e-Learning Industry Stats at a Glance

Digital/online learning has grown by 900% since 2000, making it the fastest-growing market in the education industry.
The learning management system market is expected to grow from $16.19 billion in 2022 to almost $41 billion in 2029, at a CAGR of 14.2% for the period.
Globally, the overall e-learning market is expected to achieve a value of $350 billion by 2025 with annual CAGR growth of 9.1%.
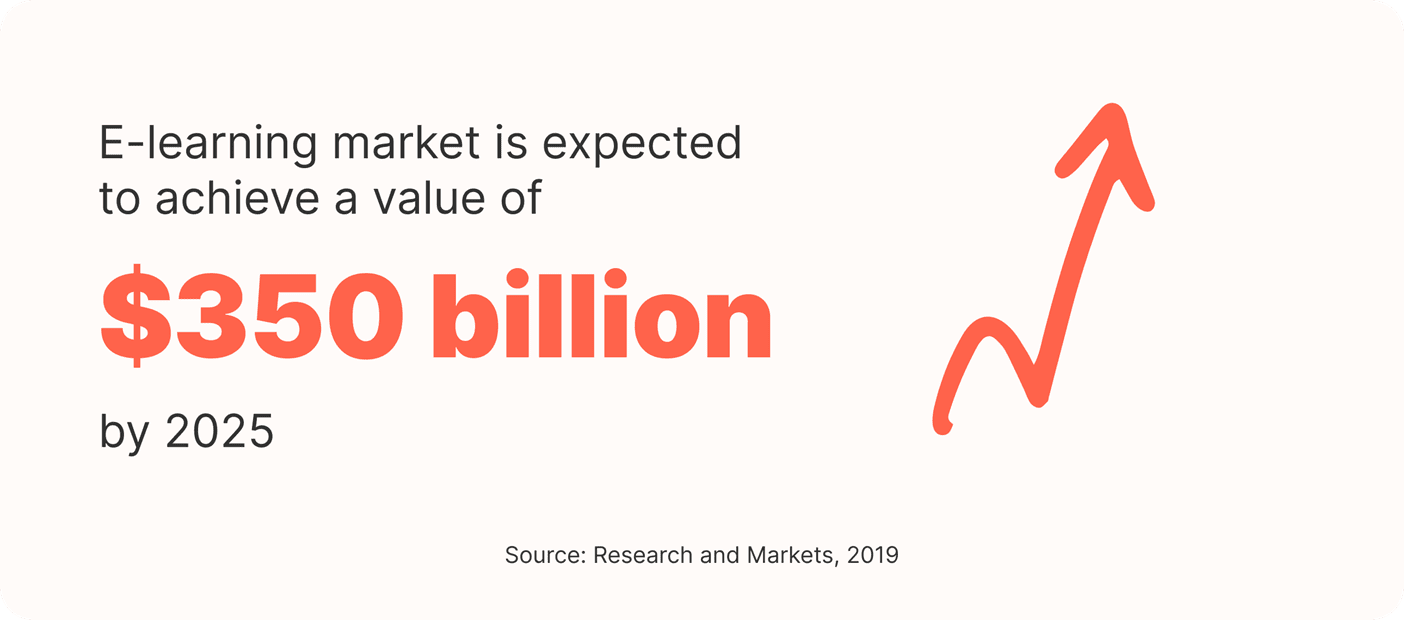
According to a study by IBM, every $1 invested in digital learning for employees brings a return of $30 for companies.
In 2020, there were more than 950 universities offering 67 degrees through major open online course (MOOC) platforms.
Moodle is the most popular LMS in the world in terms of total number of users (124 million).
2. E-Learning vs. LMS

While the two terms are often used interchangeably, there are important differences between e-Learning and learning management systems (LMS) that are worth understanding. The main differences between a straightforward e-Learning platform and a LMS are in the functionality and accessibility.
For example, an LMS allows more control over customizing course content and delivery, and tracking student progress. A LMS may offer storage, file sharing, grading, collaboration, and certification capabilities. The LMS may also only be accessible within the organization using it, or by a particular sector of learners (such as students attending a course designed specifically by their K-12 teacher on Google Classroom).
On the other hand, an e-Learning portal will simply facilitate the hosting of digital courses while providing access to anyone who wants to use them. As such, many users of e-Learning tools also have to incorporate a LMS if they want to include course management and training features that may be necessary for properly catering to the needs of their target users.
Other differences between LMS and e-Learning platforms is the time it takes to implement and the cost. LMSs are more expensive and complicated to set up. E-Learning sites are lighter and more flexible, in comparison, making them cheaper, as well as easier to launch and integrate with other learning tools.
E-learning: This is a broad term that encompasses the accessing of learning material and instructions via electronic means (internet and computers). It often involves the use of online learning software and the capacity to host live or pre-recorded audio and video, as well as text-based content that can be accessed by anyone, anywhere, and at any time.
The whole point of e-learning is to make it possible for people to access educational content without having to visit a physical classroom. This educational content can be consumed by a single individual or groups of people at a time. edX, Coursera, and Skillshare are a few examples of e-learning websites where anyone can sign up for an online course.
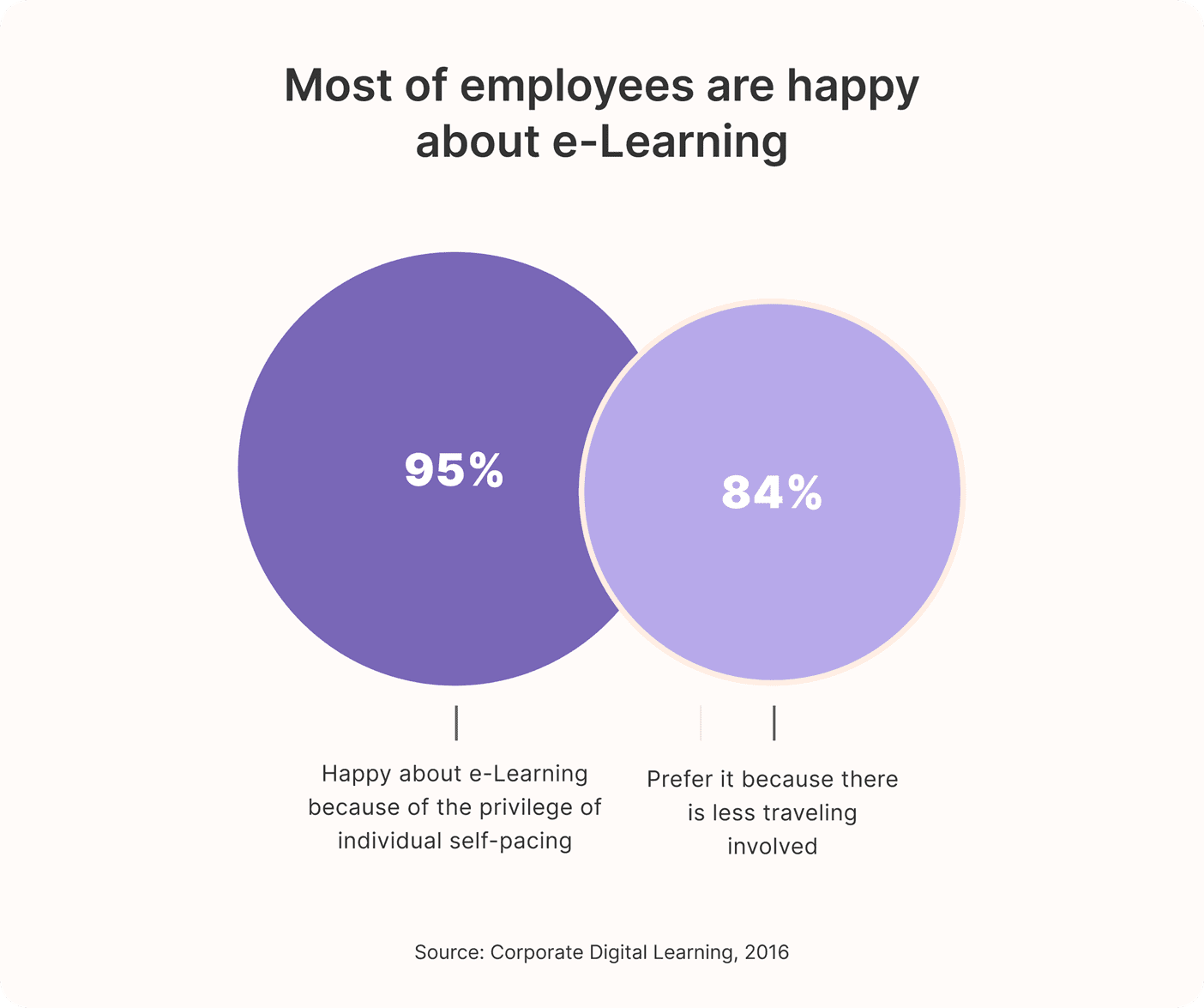
There has been rapid adoption of e-learning into the education industry over the past 25 years. 95% of employees are happy about e-Learning because of the privilege of individual self-pacing, while 84% prefer it because there is less traveling involved.
The pandemic has further accelerated the shift from physical to electronic learning. Before the pandemic hit, approximately 77% of U.S. companies offered e-learning training programs. That number jumped to 98% by the end of 2020.
Not all types of e-Learning are experiencing growth. Up to 2021, the self-paced e-Learning segment was declining at a rate of over 6% year-on-year. This, however, can be attributed to the growing popularity of micro-learning (more on that later).
LMS: Learning management systems are types of e-learning platforms. They are defined as software that can be used to administer, document, track, monitor, and even automate the learning process.
At the same time, learning management systems make it possible for students to access and use learning content, as well as complete online quizzes, exams, and surveys where applicable. Many LMSs also offer social networking tools, discussion forums, and other community features to make learning materials more interesting and immersive.
Learning management systems are split into two main types – on-site and cloud-based.
- On-site LMS: These include desktop LMS, which are software applications that must be installed on a desktop device to enable learning activities for the user; mobile LMS apps, which are designed specifically for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets; and self-hosted LMS, which are downloaded by the user often for a one-time cost or even for free. On-site LMS solutions allow for some amount of customization, but the user often has to handle maintenance on their own or pay for future updates.
- Cloud-based LMS: Cloud-based learning management systems are, as the name suggests, hosted on the cloud by their vendors. They command more than 75% of the LMS market and are operated as software-as-a-service businesses, meaning users must purchase a subscription to access all necessary functions and features. Unlike on-site LMS, cloud-based LMSs are fully maintained and updated by the vendor.
Schools, especially those offering public education, and business organizations are the main users of LMS platforms. A few of the top LMS platforms include Moodle, Google Classrooms, Brightspace, Canvas, and Blackboard.
There are more than 700 recognized learning management systems in use.
In terms of market size, the LMS market is expected to reach a value of almost $30 billion by 2025.

3. LMS and e-Learning Accessibility

E-learning is spreading rapidly among the general population. But how easy is it for school students and employees to get access to learning content? One key driver seems to be access to increasingly capable Computers & Mobile Devices and more reliable Internet Service. Faster internet and cheaper devices have made it relatively easy for most people to join web based e-Learning and LMS platforms.
As we see higher rates of access we can expect adoption rates to continue to increase. This is especially interesting because online learning also tends to make access to education and training more affordable and more flexible – both crucial determinants of personal and organizational investment in learning.
In other words, we can safely anticipate that a positive feedback loop has a high potential for forming driven by better digital access and more widespread e-learning adoption and LMS use.
Access to the internet is essential for consumption of digital learning content. 66% of the global population has internet access, and 4.28 billion are unique mobile internet users.
89% of employees partake in e-learning activities using desktop devices, including laptops (78%). At the same time, 25% reported using their mobile devices at some point.
99% of students have access to reliable devices (laptops, desktops, tablets, and smartphones) for digital learning. 72% have no issues with using these devices for schoolwork.
Using a tablet for digital learning is considered to be the most ideal for workers, as 97% of employees say tablets make it possible for online course material to be consumed at both home and office.
Smartphone usage has been found to result in a 45% quicker course completion time than using desktop devices for online learning.
4. LMS and E-Learning Adoption

Online learning has made its way into small, medium and large organizations, educational institutions, and the homes of the general population. No doubt, advancements in technology, as well as improved levels of accessibility, have helped to ensure e-learning as a whole is more readily adopted. But where are we seeing the largest growth for e-learnign and LMS use?
For now it seems that the current leaders in adoption are North America, Europe and China, while the highest growth rates are being observed in APAC.
The market with the largest number of people adopting e-learning usage is North America (United States and Canada). In 2020, this market accounted for more than one-third of global e-learning revenues.
In U.S. schools, 85% of teachers employ the use of digital learning aids to complement student lessons and exercises. Also, almost two-thirds of high school students and 45% of elementary students are using e-learning tools.
LMS use in Europe was forecasted to have a CAGR growth rate of 27% in 2020. At the same time, Europe is expected to have the second highest revenue from LMS adoption by the end of 2022.
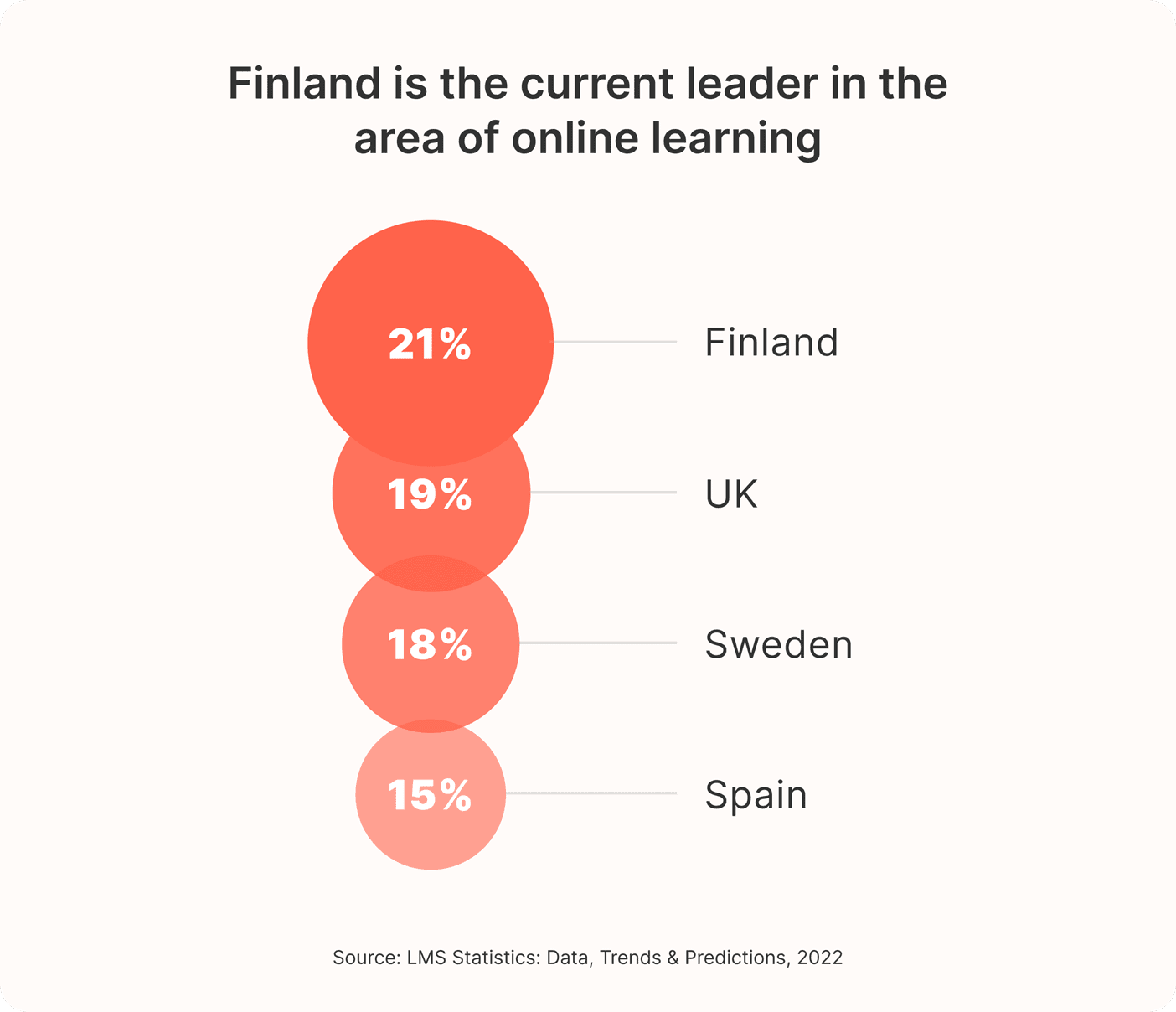
Across Europe, Finland is the current leader in the area of online learning. 21% of its population has taken at least one online course. The UK (19%), Sweden (18%), and Spain (15%), are the other European countries closest behind.
The Asia-Pacific region currently has the fastest LMS annual growth rate. This region is forecasted to have an LMS market size increase of 34.2% CAGR by the end of 2022.
China’s move to get students to study online in early 2020, resulted in what was described as the “largest online movement in the history of education.” This was after 250 million students, including over 700,000 K-12 students started attending classes via the Tencent Classroom cloud platform.
The Latin America region has seen increased LMS and e-learning adoption, and is currently ranked 4th for revenue generated from e-learning activities. An estimated 12 million people across 20 Latin American countries have signed up for at least one form of online education.
For now it seems that the current leaders in adoption are North America, Europe and China, while the highest growth rates are being observed in APAC.
The market with the largest number of people adopting e-learning usage is North America (United States and Canada). In 2020, this market accounted for more than one-third of global e-learning revenues.
In U.S. schools, 85% of teachers employ the use of digital learning aids to complement student lessons and exercises. Also, almost two-thirds of high school students and 45% of elementary students are using e-learning tools.
LMS use in Europe was forecasted to have a CAGR growth rate of 27% in 2020. At the same time, Europe is expected to have the second highest revenue from LMS adoption by the end of 2022.
Across Europe, Finland is the current leader in the area of online learning. 21% of its population has taken at least one online course. The UK (19%), Sweden (18%), and Spain (15%), are the other European countries closest behind.

It is predicted that the e-learning market in Latin America will hit $3 billion in annual revenue by the year 2023.

Africa, as a region, has one of the slowest LMS growth rates, at 15% per annum. This is partially due to lower internet penetration in some areas, among other challenges.
Revenues generated by learning management systems in Africa are estimated to be around $1 billion annually.
Almost 60% of companies have adopted the practice of BYOD (bring your own device) for digital learning, and two-thirds of employees use their personal smartphones for work-related activities, including training.
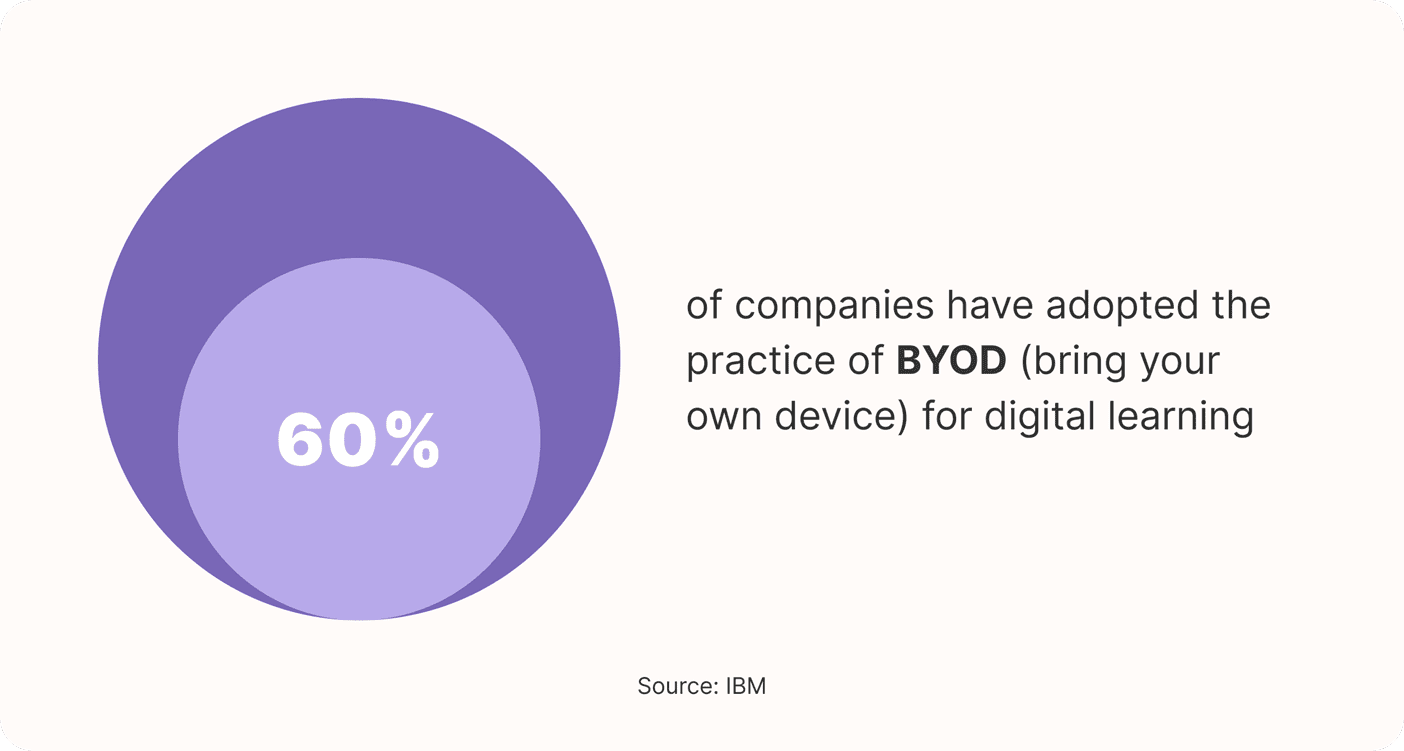
Of the organizations that have not yet embraced digital training, 93% have expressed plans to adopt online learning methods in the near future.
In terms of overall demographics, millennials are the most influential age group in LMS and e-learning adoption. 87% of this cohort see continuous career development as being important to their jobs.
More than 5.8 million college students were fully enrolled in online classes in 2020, roughly 1.5 times the 3.5 million who were doing so in 2019.
5. LMS and E-Learning Challenges

Despite the huge shift to digital learning, some challenges remain for students, organizations, and private individuals who want to benefit from online learning. For one, many e-learning platforms are not inclusive enough to accommodate the various habits of learners.
In addition, access to the internet and related technologies is still lacking or prohibitively expensive in some areas of the world where students are finding it difficult to attend classes on a regular basis.
Online learning platforms still have to leverage technology to further enhance mobile access, since plenty of people still tend to rely heavily on mobile data in order to conduct e-learning activities.
Access to a reliable internet service continues to be an issue for millions of people around the world. In the U.S., 25% of households with K-12 students lacked broadband internet access. In addition, 40% have challenges accessing educational content online due to language barriers and other obstacles. These numbers are much higher in lesser developed areas, such as some countries in Africa and the Middle East.
More than 80% of learners believe inability to afford or gain access to e-learning technology will lead to heightened education inequality.
At the height of the pandemic, the vast majority of students in American public schools had to switch to online lessons. However, in 2020, less than 25% of public school teachers in the U.S. were able to confirm that all their students had computer access.
Many organizations are not entirely sure how e-learning is impacting their bottom line. 33% of Learning and Development (L&D) teams do not measure the impact of online learning, 53% deem their measurement practices to be inadequate, and only 14% think they are measuring its impact effectively.
41% of educators in the U.S. pointed to a lack of having related technical training as a major deterrent against increasing digital education technology in schools.
Some working professionals find it difficult to complete online training on their own without a structured learning schedule (such as what exists in a traditional school system) because the average employee can only afford 24 minutes per week for learning.
Implementing e-Learning technology can be costly and time-consuming. 34% of LMS buyers, for example, said implementation did not go as expected.
6. Impact of COVID-19 on the LMS and eLearning Industry

The covid-19 pandemic saw a sudden influx of people wanting to use virtual learning services. LMS and e-learning industry stakeholders were able to pick up the slack from closed school doors, for the most part.
What’s more interesting is that despite restrictions to public spaces being eased as we approach the second half of 2022; enough of a shift has occurred towards hybrid attendance and distance learning/training that it’s likely to stick for a long time to come.
According to the World Economic Forum, more than 1.2 billion students in 185+ countries could not attend school in the early months of the pandemic, resulting in increased reliance on LMS and e-learning platforms to deliver lessons and other course material.
In March 2022, UNICEF announced that 23 countries with more than 405 million students were yet to fully reopen schools.
Upwards of 60 million new users joined Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platforms in 2020 alone.
In response to the changing learning needs of the population, e-Learning platforms rolled out 360 new micro-credentials in 2020, bringing the total to over 1,100.
As companies closed their doors and were only able to operate with employees working from home, 23% of organizations expanded their budgets for online training during this time.
With the high unemployment rate during the first half of the pandemic, many people took the time to improve themselves through e-learning. edX, which is ranked as the second most popular MOOC platform in the U.S., experienced a 161% increase in new registrants between November 2019 and November 2020.
7. New LMS and e-Learning Trends in 2023

Digital learning will be increasingly relied upon to meet the learning needs of today’s students and employees. Many of the companies welcoming workers back to the office, for instance, have sought to implement a mixed mode of attendance, with employees working remotely some days of the week.
On the other hand, schools are trying to balance in-person and online learning in order to bridge the reported learning divide brought about by the two-year old pandemic. In response, digital learning tools will continuously need fine-tuning and updating to accommodate the various individual needs and educational situations that are arising post-pandemic.
What is this looking like for 2023 and beyond? E-Learning solutions are seeing changes surrounding emerging technologies that impact human learning habits.
More learning communities
It is not coincidental that online communities experienced a boom at the same time digital learning took off during the pandemic. Learning platforms are realizing that it is not enough to simply provide access to learning content. LMS solutions such as Moodle, Adobe, and TalentLMS are incorporating a community aspect to make learning more immersive and engaging for their users.
According to Higher Logic, pairing LMS with community management tools can help organizations differentiate their online learning delivery from the competition.
The sharp growth of Moodle has been boosted by the presence of several community forums. Over 702 million forum posts have been recorded on the platform to date.
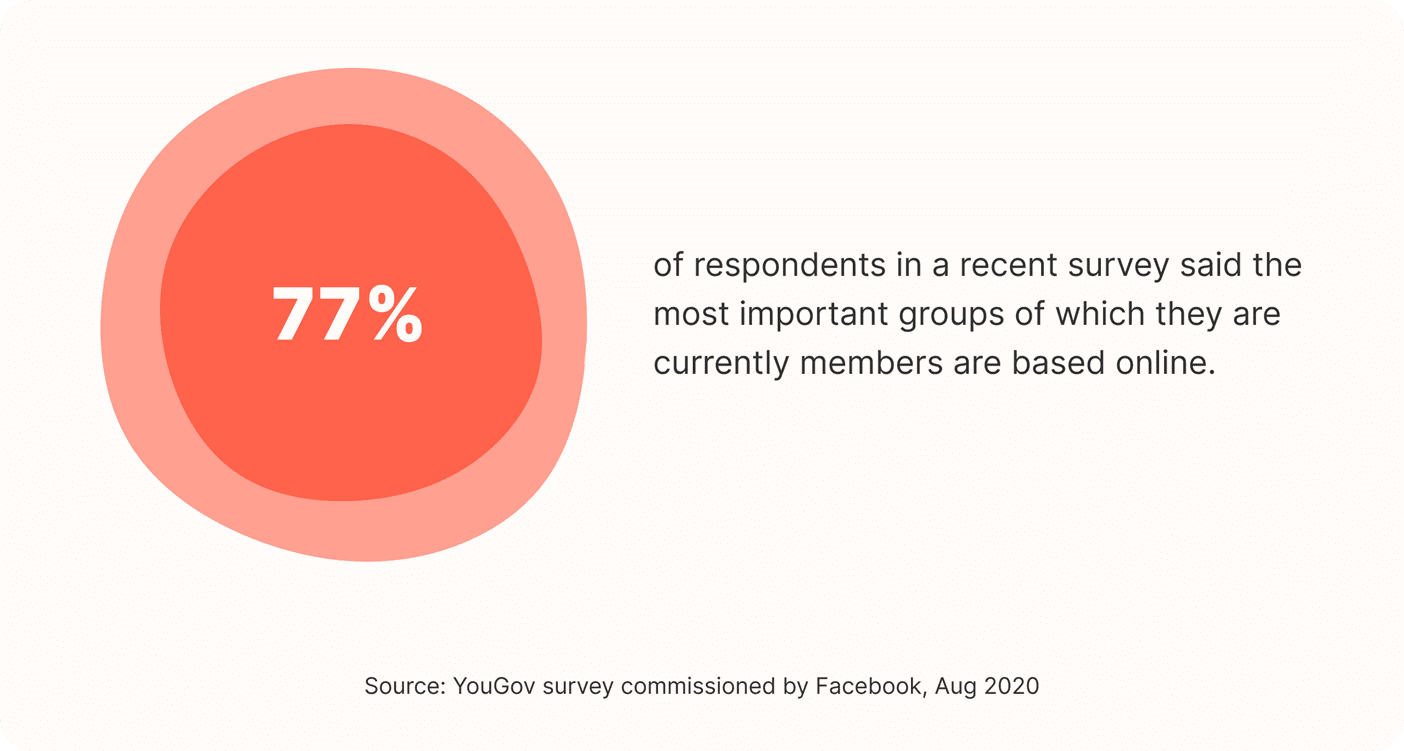
77% of respondents in a recent survey said the most important groups of which they are currently members are based online.
Social learning, which promotes interactive and collaborative behavior, is increasingly being utilized in e-Learning programs. More than 50% of L&D professionals are already including social learning elements into their digital learning offerings.
In addition, while typical MOOC programs tend to have low completion rates – single digits in some cases, a Harvard study found that social learning and collaborative features pushed completion rates above 85%.
Leading companies in the LMS space using community to empower learners
- Edoome — Edoome connects teachers with their students so they can communicate, collaborate and share, and provides tools for teachers to help them save time in planning, assessing and keeping track of their students’ progress all in just one place.
- Xperiencify — Most online courses are designed to be done in isolation. There’s no feedback. Not from the course creator. Not from other students. And that’s demotivating. Xperiencify incorporates fun ways for your students to get important social approval & feedback and have a little fun too.
- Eduflow — Eduflow is built around the concept that learners thrive when they collaborate, give feedback, and work together. Their LMS enables peer review, active discussions, group work, and instructor review.
Mobile learning
As mentioned earlier, more students are completing course activities either fully or partially with their smartphones and tablets. This trend is expected to continue in 2023 and beyond.
70% of mobile e-learners say using a mobile device makes them feel more motivated to learn than using a laptop or desktop computer. 72% say they experience more engagement with learning modules when accessed from a mobile device.
Mobile learning is growing at an annual rate of about 20% and is expected to reach a market value in excess of $80 billion by 2027.
Leading companies in the LMS space using mobile learning
- Blackboard — The Blackboard App gives students the information they want, the connections they crave, and the personalization they demand, on the go. Blackboard puts learning directly in the hands of students, so they can stay connected with their educational journey anytime, anywhere.
- Matrix — Instructors use Matrix to design high-quality courses for their learners. The learning experience is enhanced with their mobile first app, which allows users to enjoy a great learning experience anytime, anywhere.
- Docebo — Docebo’s mobile app was designed to create a frictionless, uninterrupted experience for your learners. Learners can even take training courses while offline, with progress automatically tracked and synced with their Docebo LMS when back online. Docebo’s mobile app is not limited to any plan type, and is accessible to all users.
Gamification
Gamification aims to provide a more engaging and interactive experience for online learners and is one of the essential ingredients when building digital learning communities. It borrows from the mechanics used in video games to help users feel more involved and retain what was taught, as well as to encourage healthy competition.
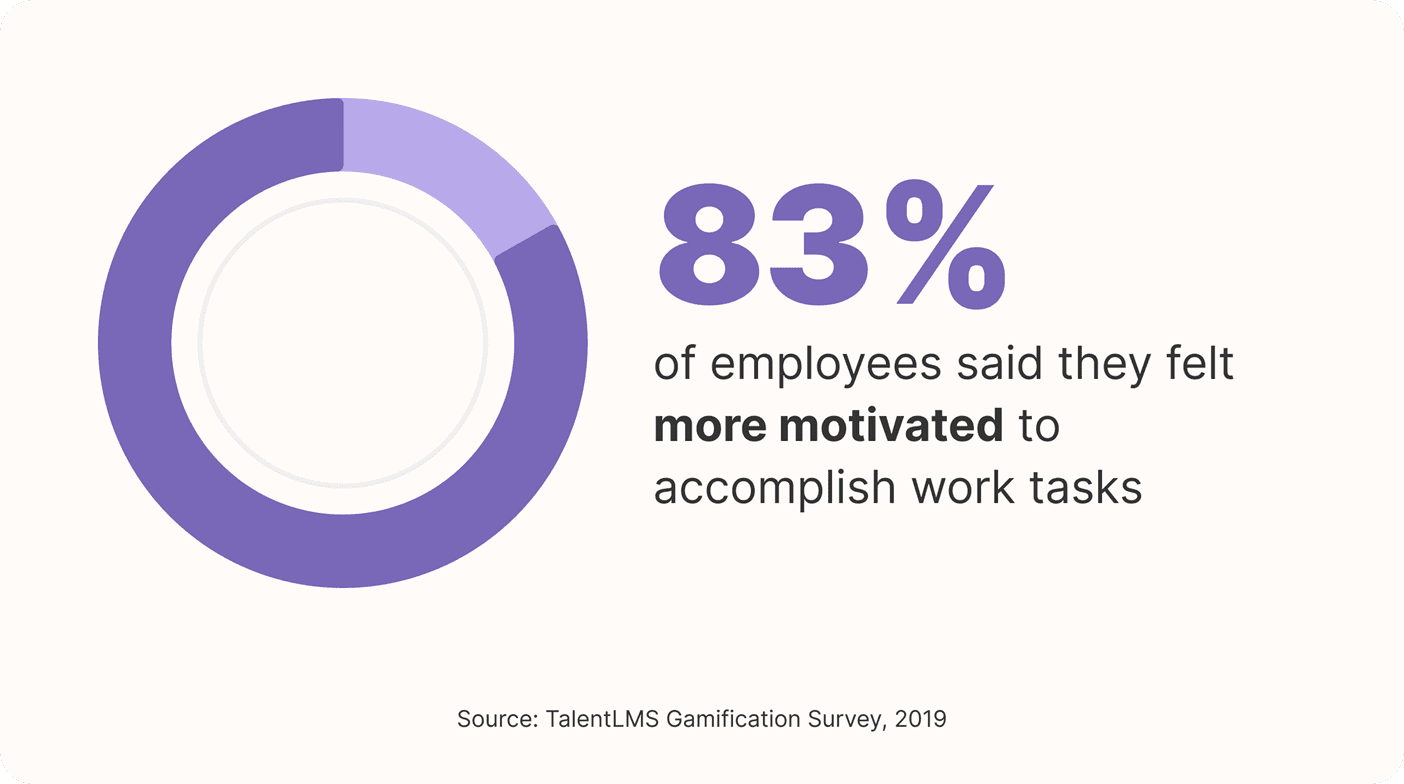
After receiving game-based training, 83% of employees said they felt more motivated to accomplish work tasks. Less than 20% of LMS users have access to game-based learning, but 26% of learners would like to have this feature.
Digital learning communities, when paired with gamification, can see increased engagement of over 150%.
According to EdTech Magazine, game-based learning prepares K-12 students for success in a digital future where concepts such as the metaverse will flourish.
The game-based e-learning market is expected to generate revenues of over $28 billion by 2025.

Leading companies in the LMS space using gamification to enhance learning
- Syllabus — Syllabus is an LMS platform that promotes gamification, allowing companies to reward their learners with exciting prizes to keep them engaged and motivated.
- Tovulti LMS — An LMS that allows instructors to reward their learners by allowing them to earn badges and showcase them on their profile.
- ELB Learning — Games make learners active participants in their training. Instead of passively clicking through training materials, ELB eLearning games drive learners to interact and use their skills to overcome challenges.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence, including machine learning, is already being implemented in some digital learning platforms. This technology allows LMS platforms to better understand learners’ preferences, and create more personalized teaching methods.
It is expected that, by 2024, AI will be a major function in 47% of all LMS platforms.
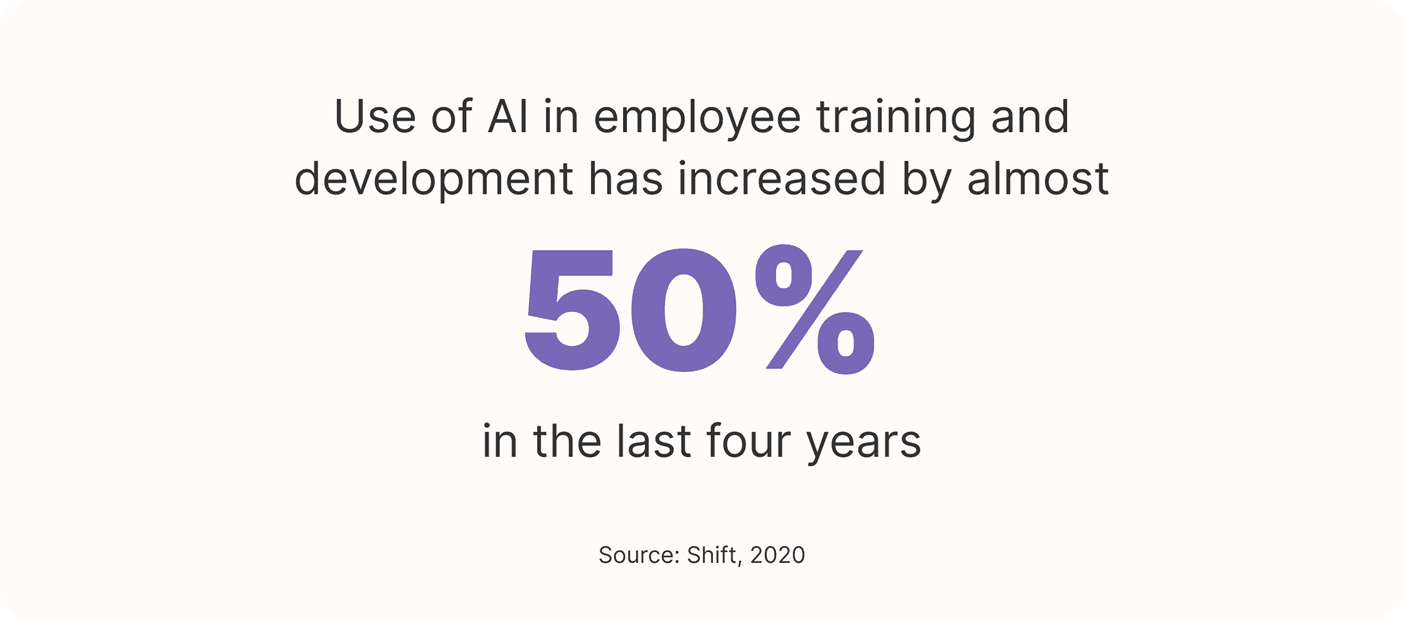
According to Shift, use of AI in employee training and development has increased by almost 50% in the last four years.
By 2025, overall investment in AI-driven e-Learning is forecasted to surpass $190 billion.
Duolingo, a language-learning community with over 500 million users worldwide, is a popular example of an e-Learning platform that makes use of AI. It uses lifelike chatbots that help users practice.
Leading companies in the LMS space using AI
- Absorb Intelligence — AI-powered LMS with custom set of capabilities designed to simplify admin tasks and give your learners more opportunities to gain new skills and knowledge. System enhances search and microlearning and improves administrative efficiency, all through predictive AI and natural language recognition.
- Twilight LMS — Through AI integration, instructors are able to check the behavior reports for every student and have access to their course-related chatrooms as well.
- Stream LXP — Provide unique insights to improve collaborative learning using Natural Language Processing techniques and the latest AI.
Immersive learning experiences
People are craving more immersive experiences in every aspect of life, including online communities and e-Learning. More digital learning platforms are investing in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality, and extended reality (XR). Using these immersive experiences, trainers can make it easier for learners to grasp complex concepts, as well as increase engagement with the course content.
The market for AR and VR learning software is expected to see revenue growth of over $700 million by 2025.
L&D managers view AR and VR as being the best all-round learning solutions to assist employees in grasping safe ways to complete tasks in their working environments.
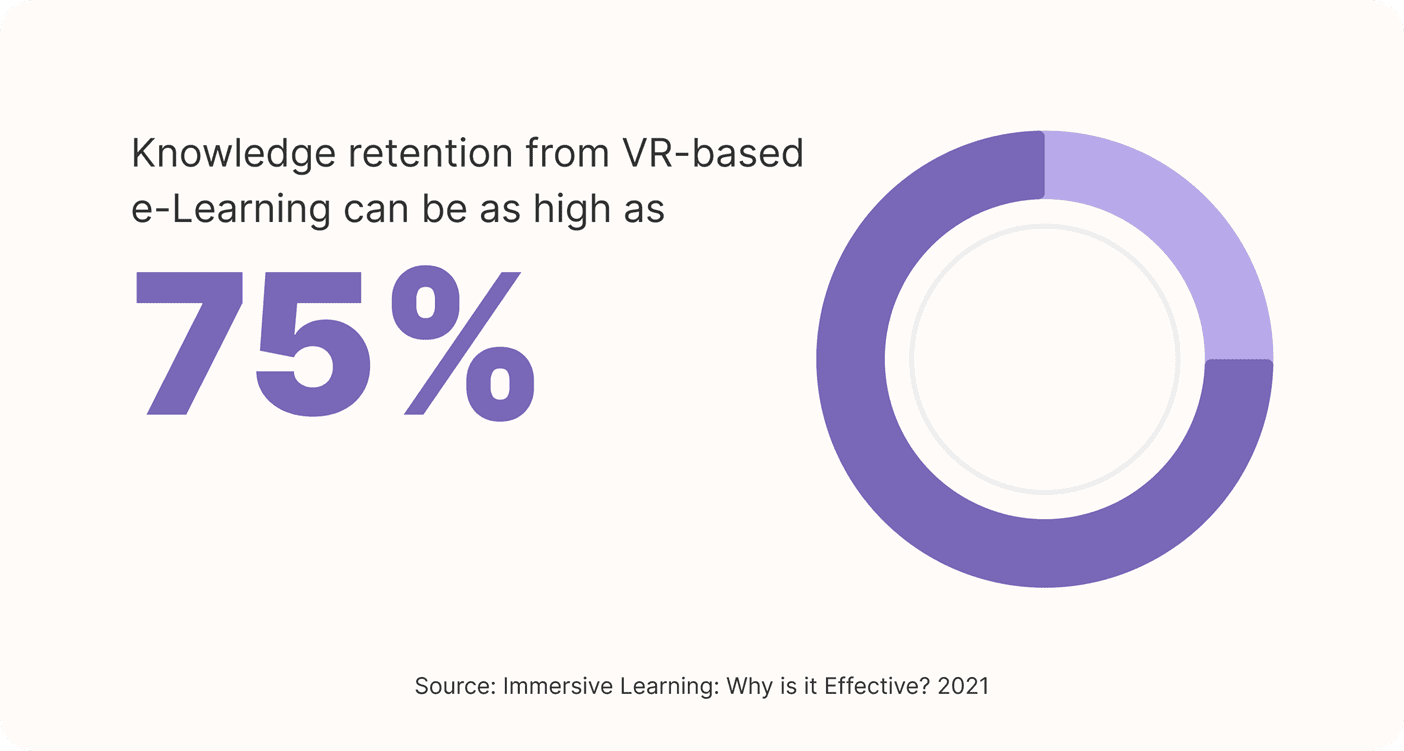
Knowledge retention from VR-based e-Learning can be as high as 75%.
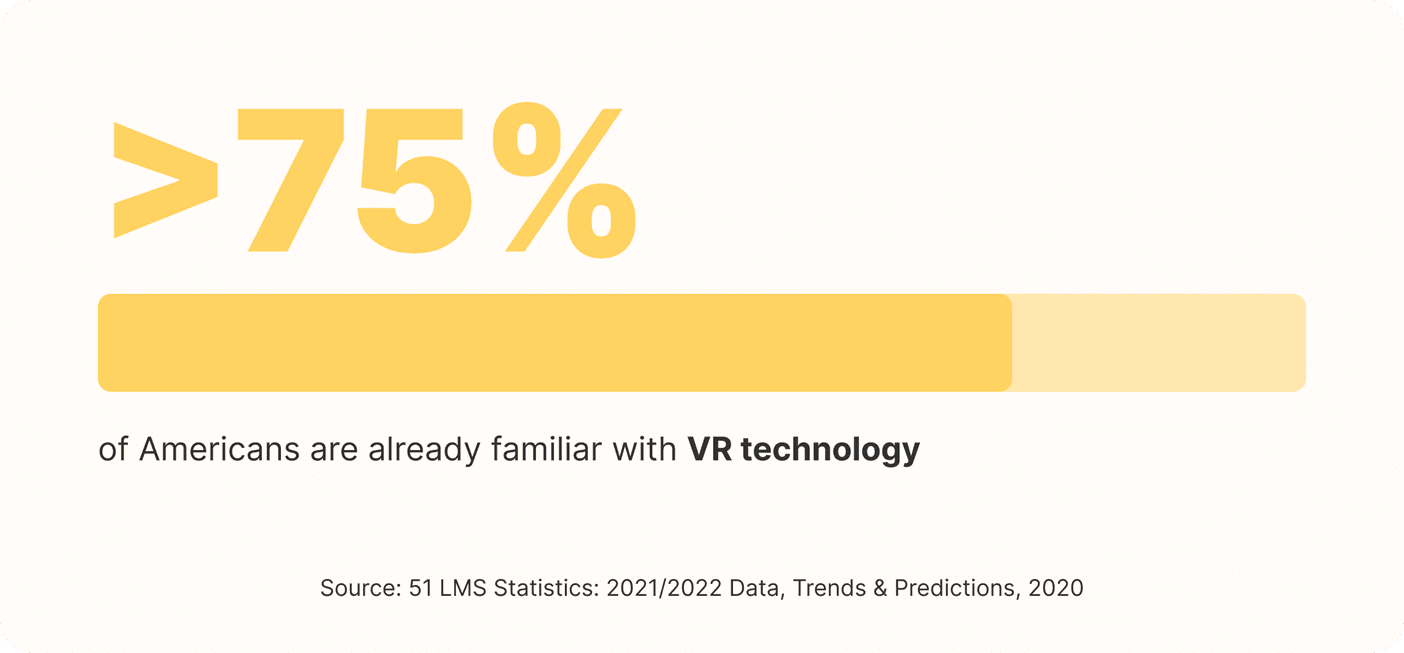
More than 75% of Americans are already familiar with VR technology.
Leading companies in the LMS space using AR and VR for immersive learning experiences
- Abara LMS — AR and VR thrive on delivering an immersive experience. Abara LMS is an award-winning platform recognized for its UI, UX, features, and user-friendly pricing, designed with an eye toward future AR and VR applications.
- Surgical Science — Surgical Science is a leading supplier of virtual reality simulators for medical training. Surgical Science’s simulators are used by medical training centers and institutes worldwide for practice, validation and certification of students, surgeons, and medical doctors.
- Engage Metaverse Platform — Engage is a spatial network solution for enterprise clients to build their own unique virtual world “MetaWorld” which can be used for employee on-boarding, training, product demos, wellbeing, customer outreach and professional events.
Video-based e-learning
Audio-visual content is among the most popular types of digital tools used in online courses and that trend is also expected to continue throughout 2022 into the future.
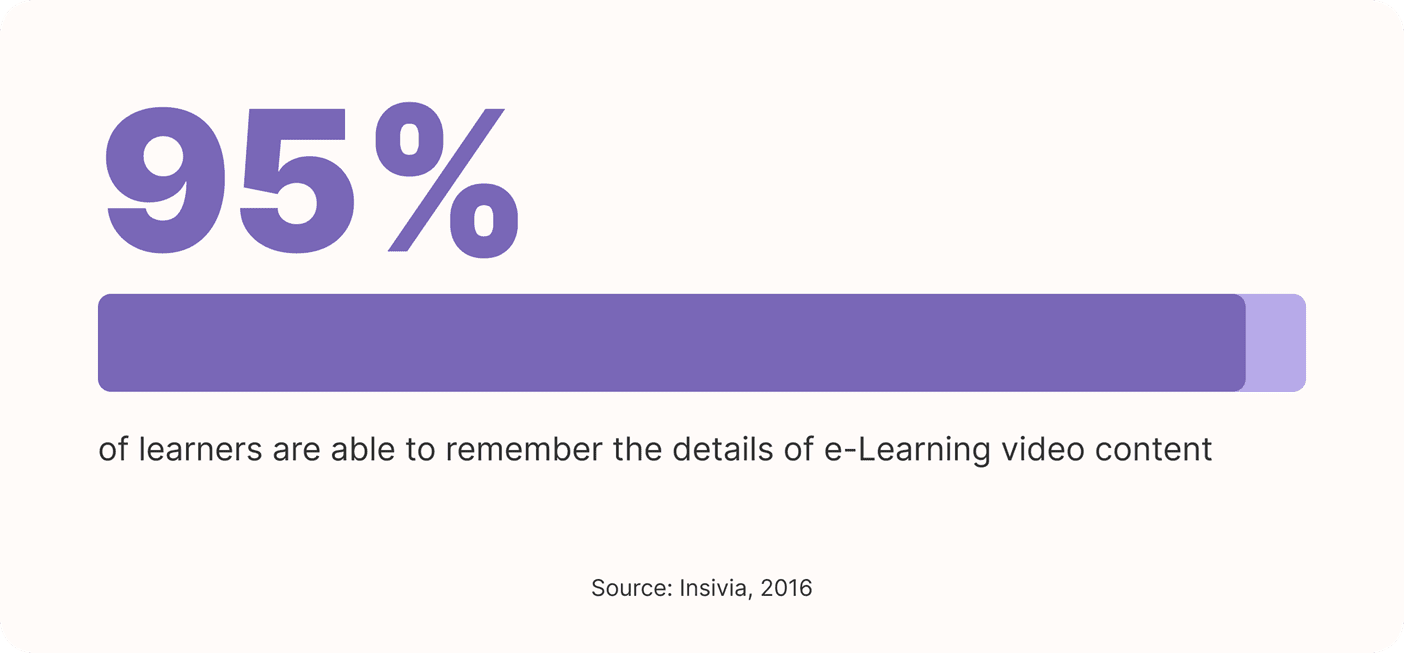
People generally find videos to be more engaging, but on top of that, 95% of learners are able to remember the details of e-Learning video content.
Three in every four employee prefer video-based material over text-based learning content.
Educational video content is among the most common digital learning materials used by K-12 students.
80% of online traffic worldwide consists of videos.
Leading companies in the LMS space using video to enhance learning
- LearnWorlds — An online course platform for creating, selling and promoting your online courses. LearnWorlds allows users to convert their videos into exceptional experiences with automatically extracted transcripts, quizzes, and tables of contents.
Micro-Learning
Micro-learning aims to address the culture of low attention span, as well as the lack of time for busy professionals to complete long courses.
The decline in self-paced e-Learning, mentioned earlier, is partially attributable to the rise in micro-learning courses, as well as more learners preferring the interactive nature of learning communities. More digital platforms are, therefore, building collaborative communities in tandem with courses that contain bite-size lessons (3 – 7 minutes long).
Micro-learning has a long-term retention rate of up to 80%, which is far greater than the 10 – 15% retention rate of traditional learning methods.
Four out of five employees believe they would learn better if they received multiple, short lessons instead of long, formal courses at the workplace.
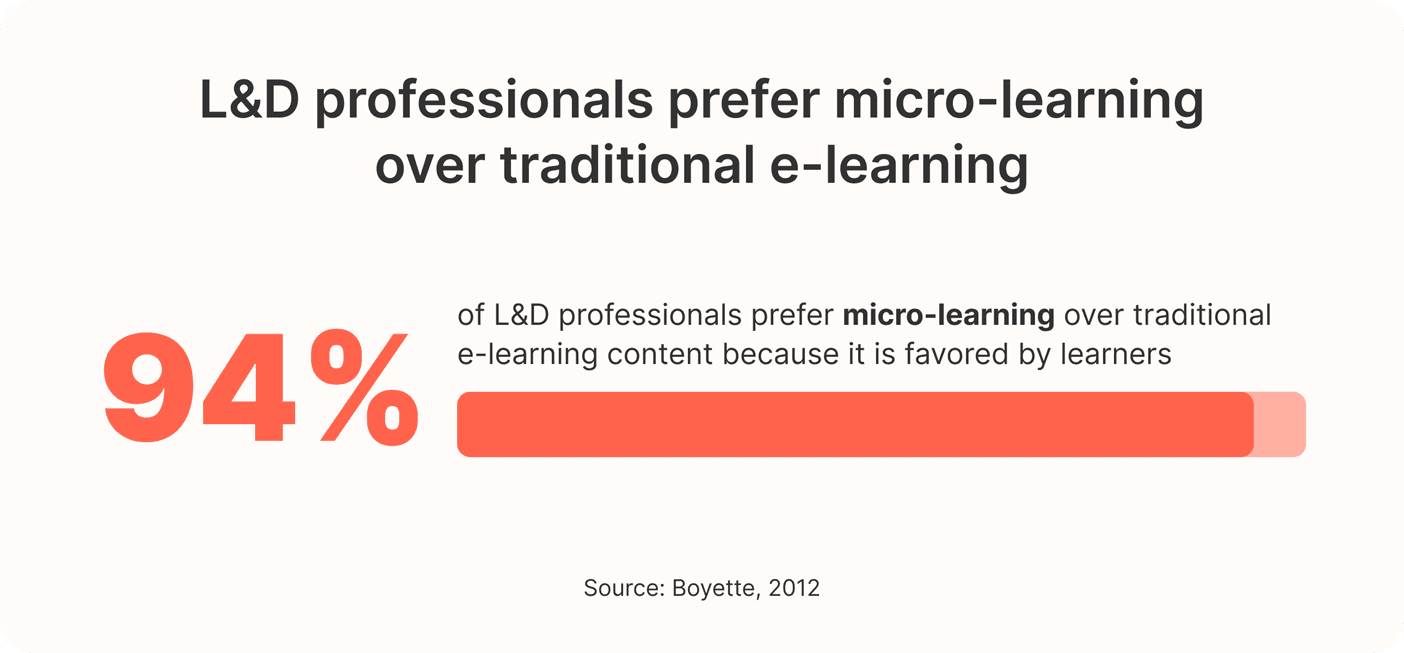
94% of L&D professionals prefer micro-learning over traditional e-learning content because it is favored by learners.
A maximum length of 3 – 7 minutes is preferred in educational videos by online learners.
Leading companies in the LMS space targeting micro learning
- EdApp — Offers employees training, learning, and development through a mobile LMS. It’s a dedicated system that uses smartphone technology and microlearning to deliver learning strategies that provide better results than desktop eLearning. It’s also about being able to use gamification to motivate learners in a way that feels natural to them… while making sure they genuinely enjoy lessons.
- TalentCards — TalentCards is a mobile learning app that uses the power of microlearning to make an impact on users. In just minutes a day, employees can learn and reinforce important training topics.
- Easygenerator — E-learning authoring tool that enables anyone, from e-learning professionals to subject-matter experts, to create and share interactive content. Easygenerator courses work on all modern devices, screen sizes, and orientations by default.
Benefits of e-learning and LMS
The move from face-to-face training to online learning has had a huge impact on both students, organizations, and independent instructors. What are some of the main benefits that have been realized?
On average, employees experience a 15 – 25% jump in productivity as a result of e-learning activities.
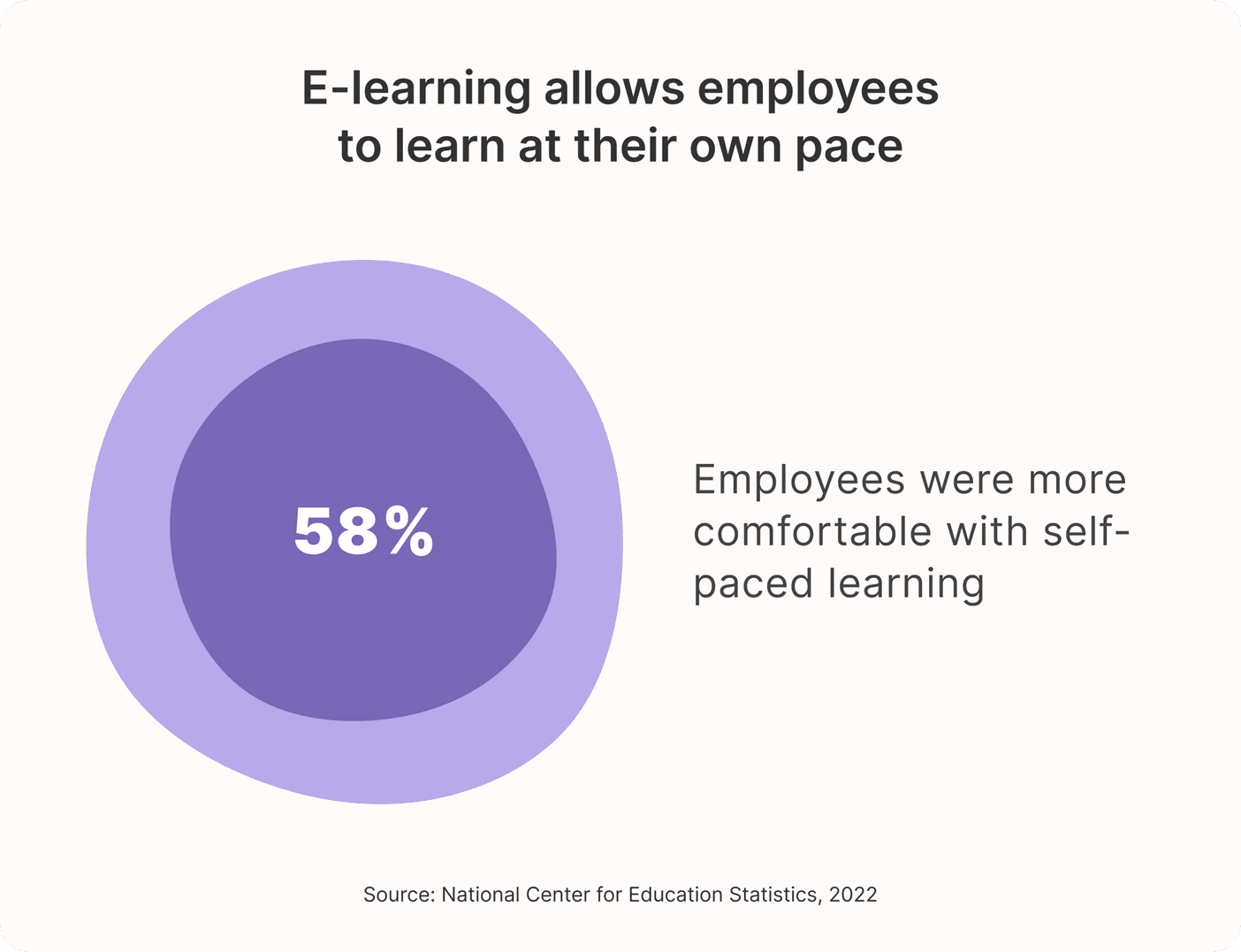
E-learning is generally more beneficial to employees because it allows them to learn at their own pace. 58% of employees in a study agreed that they were more comfortable with self-paced learning.
For students, most online learning methods require 40-60% less time to complete when compared to learning in a traditional classroom.
According to a recent report, e-learning contributes to an 18% increase in employee engagement.

A survey by the American Society for Training and Development found that firms with comprehensive training programs report increased revenues per employee by as much as 218%, as well as a 24% jump in profit margins.
72% of organizations report e-Learning helps them to keep up with technology changes, thereby allowing them to have a competitive edge.

Research by UTEP Connect found that students are able to get five times more work done while doing online courses, as compared to face-to-face learning. In addition, students retain five times more of what was taught in an online class, compared to learning in a traditional classroom.
More than 90% of company managers agree that online learning can help to close skill gaps in work teams and 60% of employees worldwide believe that e-learning makes it easier for them to adapt to change in the organization.
In addition to the earlier note that online learning leads to significant reduction in CO2 emissions, online learning can reduce energy consumption by as much as 90%. Also, it is important to note that online learning eliminates paper usage, which is important since that material makes up 60% of the waste generated by schools.
E-learning has been found to increase retention rates to 82% on average.
Companies that invest in e-learning for their staff members can expect to receive massive savings over the long-term. IBM, for instance, realized savings of $200 million after embracing e-learning for its employees.
8. LMS and E-Learning Usage Statistics

Online learning is, no doubt, revolutionizing the way people gain knowledge. Whether it is employee training, academic lectures, or privately taken courses, anyone can now advance their knowledge without the confines of a classroom or a physically present instructor. People from all walks of life, including academic scholars, company managers, CEOs, independent contractors, hobbyists, etc. are able to partake in digital learning.
Usage of online learning tools is buoyed by the fact that people can get an education or learn a new skill without having to face the horrors of traffic, crowded school environments, or increasing gas prices. What’s more, some e-learning programs allow you to learn at your own pace, and many make it possible for users to become part of collaborative and social learning communities.
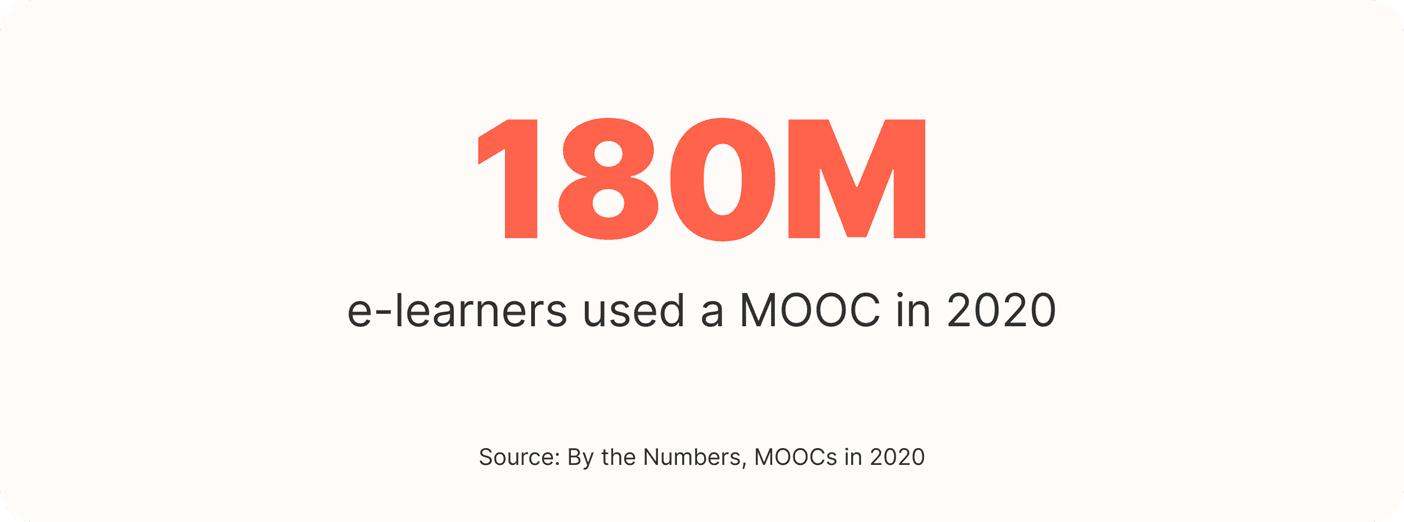
Overall, 180 million e-learners used a MOOC in 2020.
More than 90% of corporations now use e-learning methods for training and development of employees. In 1995, that number was less than 5%. (KPMG)
More than 40% of Fortune 500 companies use digital learning methods to train staff.
Currently, organizations with employee populations of between 200 and 1,000, see 37% of their L&D budgets being invested in e-learning. That figure climbs to 50% for corporations with 10,000 or more employees.
Student enrollment for online learning in the U.S. has increased every year over the past 14 years. At the same time, college enrollment has declined every year for the past 10 years.
More than half of college graduates in the U.S. think online learning at the college level is better than in-person learning.
One-fifth of American college students complete course-related activities using only a mobile device (smartphone or tablet).
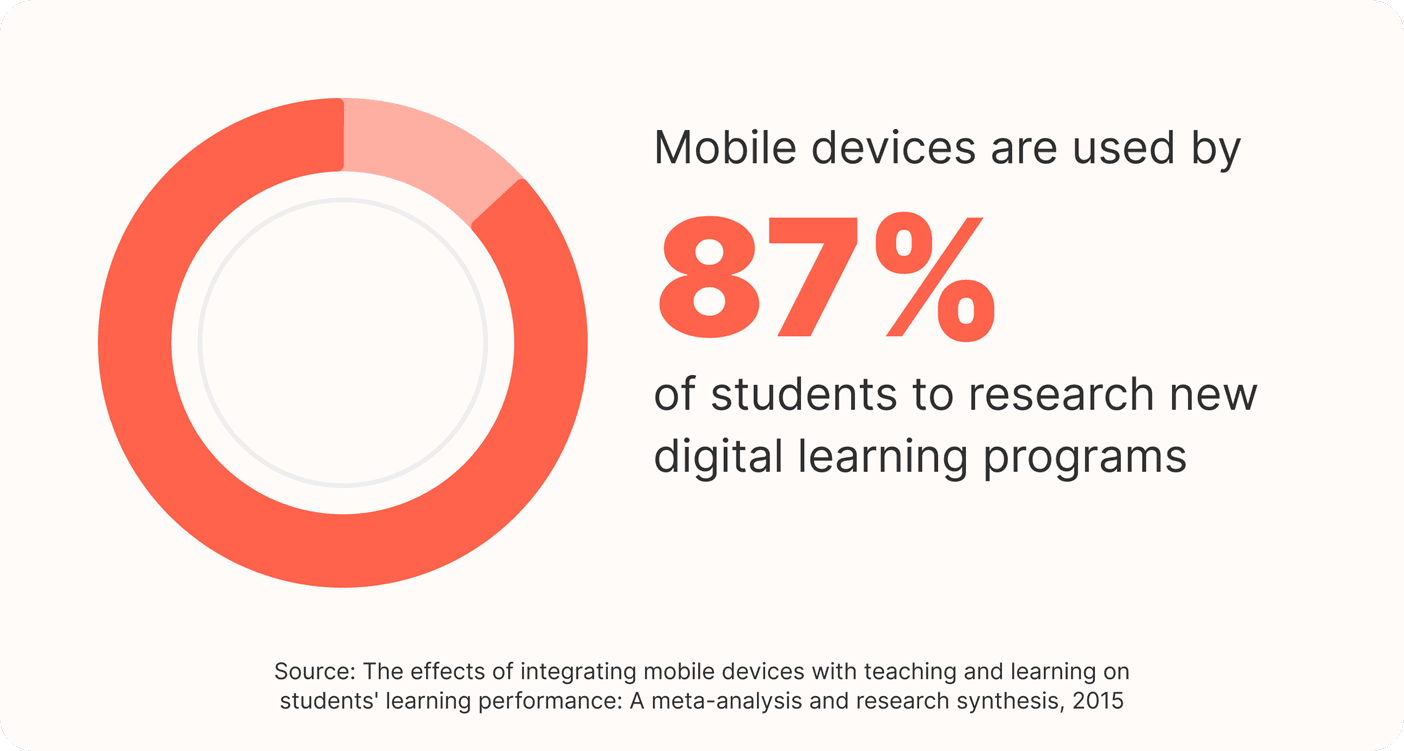
Mobile devices are used by 87% of students to research new digital learning programs.
90% of the top 25 universities in the U.S. now offer free online courses.
Over 50% of the people using MOOC platforms in the U.K. are educated to at least the degree level. 44% have a postgraduate degree.
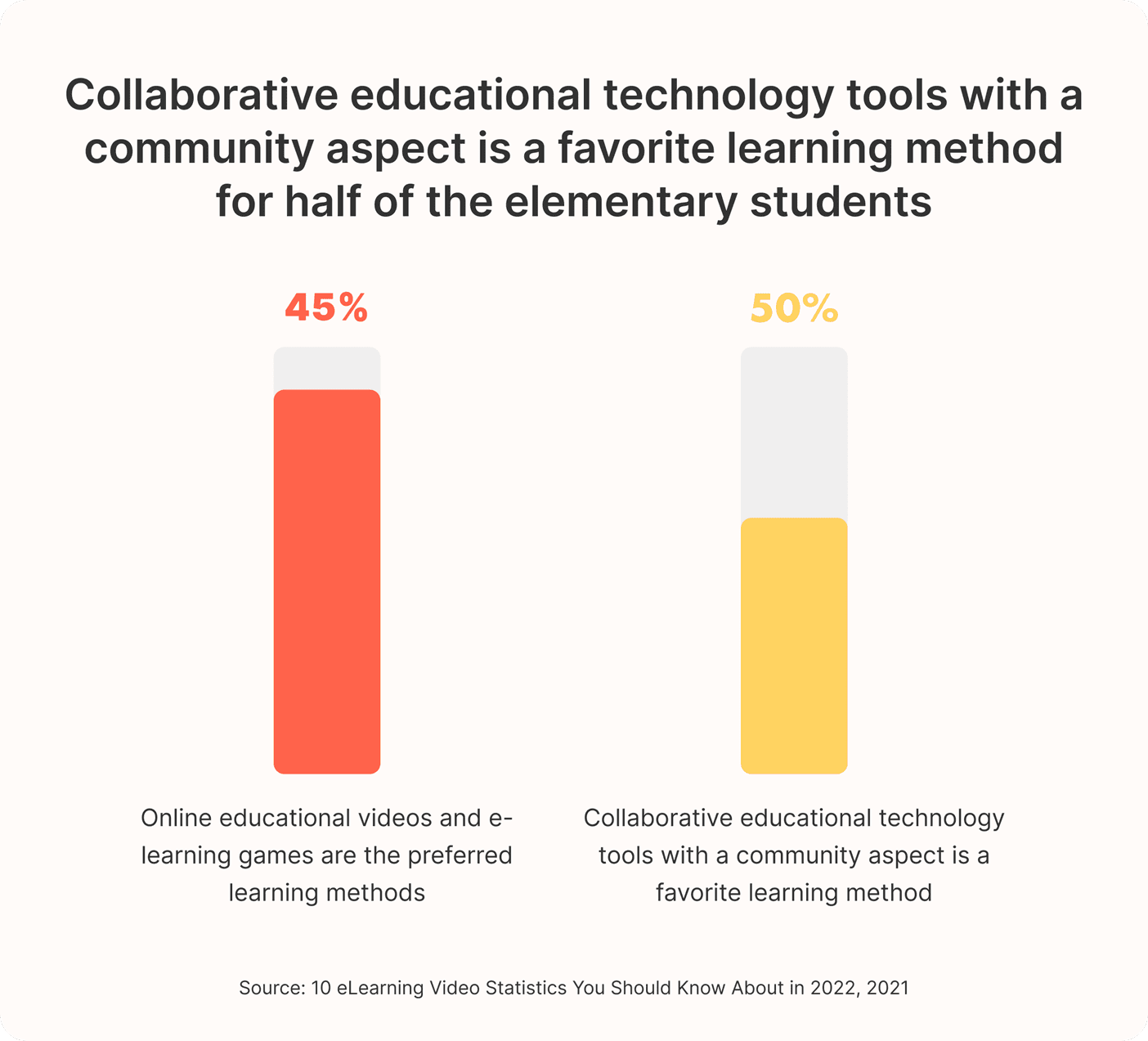
Online educational videos and e-learning games are the preferred learning methods for 45% of elementary students. Collaborative educational technology tools with a community aspect is a favorite learning method for 50%.
Educational cloud-based collaborative tools are currently used by 72% of K-12 students. At the same time, half of all teachers in K-12 classrooms take professional training courses online.
According to EdSurge, Over 50% of all criminal justice and nursing students who go on to pursue a Master’s degree, do so fully or partially online.
In excess of three million students now pursue higher education programs fully online. Almost four million post-secondary students are pursuing a minimum of one distance education program online.
Tech companies account for 30% of all LMS users, while institutions in the education industry account for another 21%.
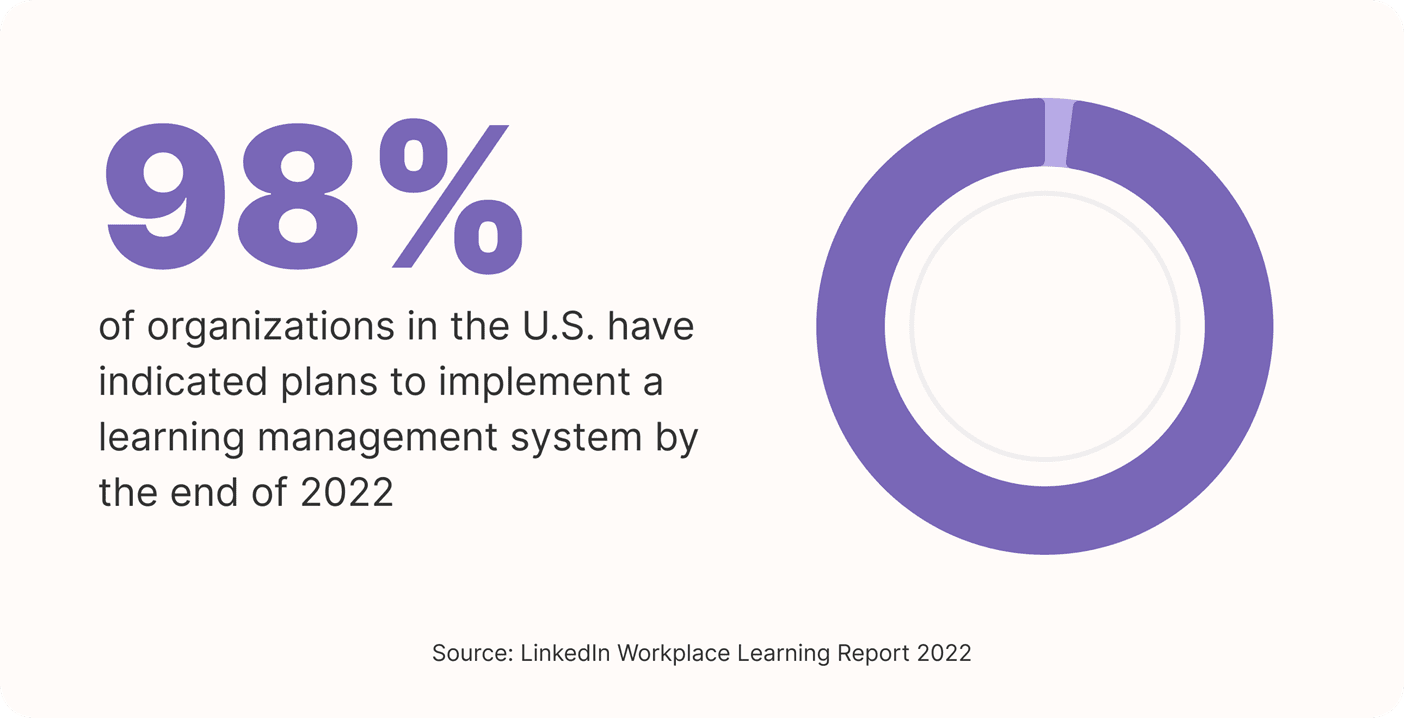
98% of organizations in the U.S. have indicated plans to implement a learning management system by the end of 2022.
Conclusion
This overview of LMS and e-Learning statistics is intended to help establish a clearer picture of what is happening in this area of the education industry.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, more people than ever now take classes online. At the same time, students and professionals are naturally being drawn to digital communities.
This creates a case for e-Learning developers to fuse online education with community components. Emerging technologies such as gamification, artificial intelligence (AI), and virtual reality makes it all entirely possible.
Implemented correctly, LMS and e-Learning software products will be better poised to meet the varying needs of users across the world. More learners will likely be able to get a personalized learning experience that helps them to achieve their learning goals.